Version Control (Git)
Version control with Git integration is only available in Crawlab Pro.
You can integrate Git, the most popular version control system, to Crawlab for team collaboration, version control and CI/CD. With Git integration, you can manage your Git repositories and spiders in a single place. This will be extremely helpful for team collaboration and version control, and ultimately improve your development efficiency.
Git Repository Management
Crawlab supports basic Git repository management. You can create, switch branches, pull code, push code and edit code in the Git repository.
Clone Git Repository
If you have existing Git repositories, you can clone them to Crawlab by following the steps below.
- Navigate to the
Git Repolist page. - Click the
New Git Repobutton.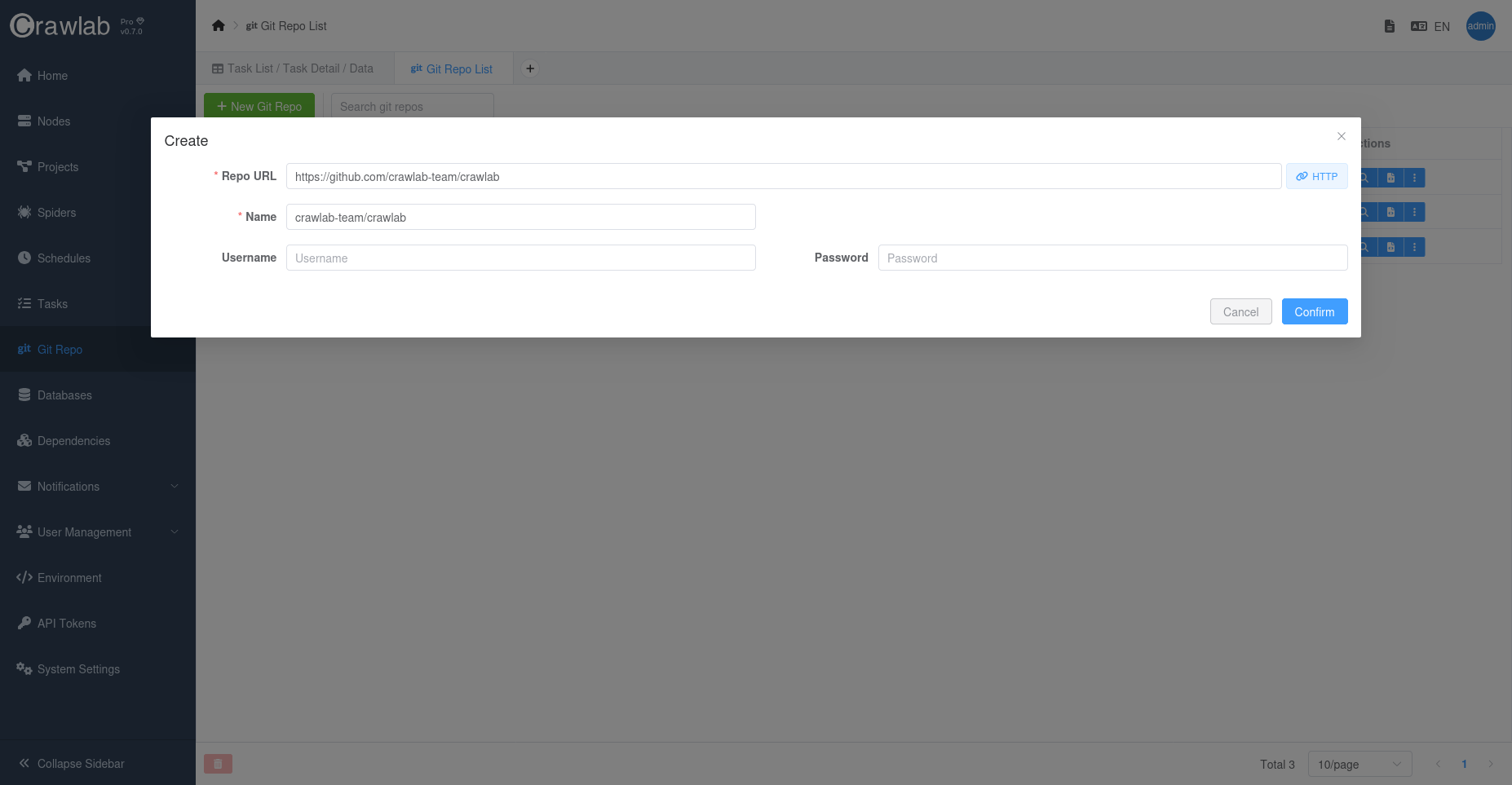
- Enter the URL of the Git repository, and the system will detect whether it's HTTPS or SSH.
- Enter the username and password for the Git repository or SSH key.
- Click the
Confirmbutton. - The system will start cloning the Git repository.

- Wait for the repository to be ready.
Switch Branch
Sometimes you may want to use non-default branch for your spiders. You can switch to a different branch by following the steps below.
- Navigate to the
Git Repolist page. - Navigate to Git Repo detail page once it's ready.
- Click on the branch selection dropdown in the middle of the action bar.
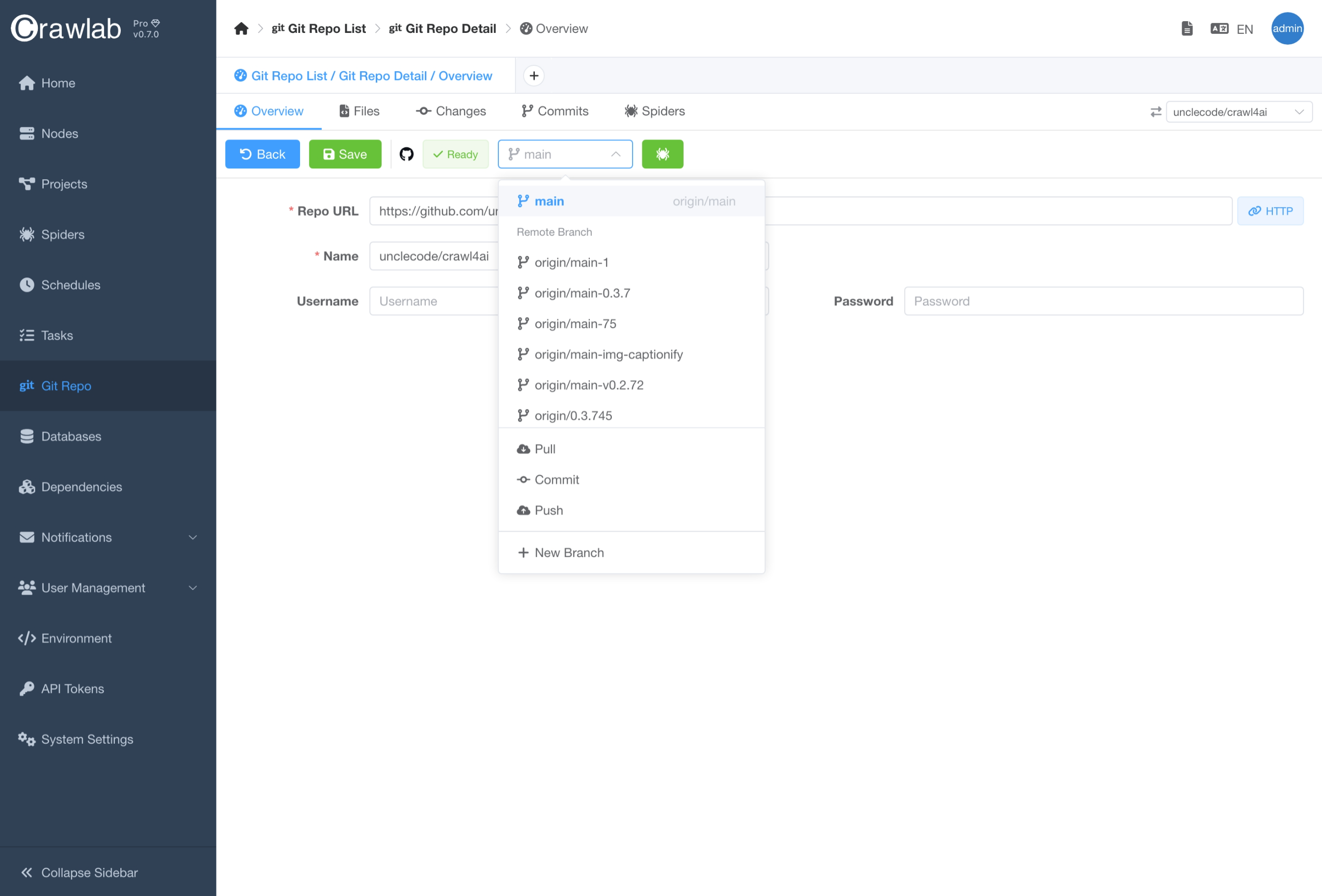
- Select the branch you want to switch to.
- Wait for the branch to be switched.
Pull Code
If your remote repository has new commits, you can pull the latest code to Crawlab by clicking the Pull button in the
Changes tab.
Edit Code
You can edit the code in the Files tab. This is similar to the code editor in the spider
detail page.
Commit/Rollback Changes
Once you have made changes to the code, you can commit/rollback the changes like you do in a Git repository.
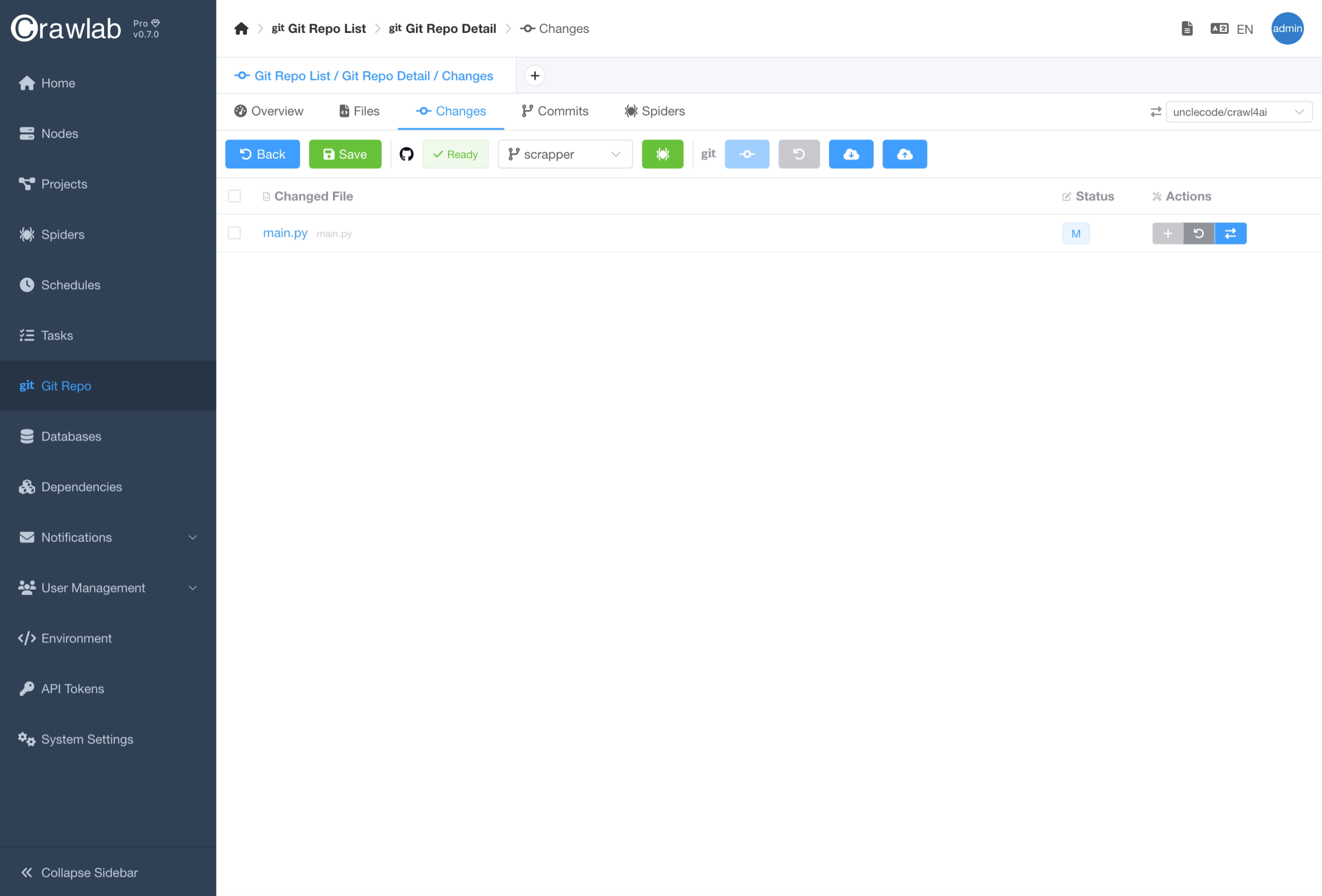
- Go to the
Changestab. - Check the files you want to commit/rollback.
- Click the
CommitorRollbackbutton and confirm. - The system will commit/rollback the changes in the local Git repository.
- You can also view the diff of the changes by clicking the
Show Diffbutton of the file you want to view.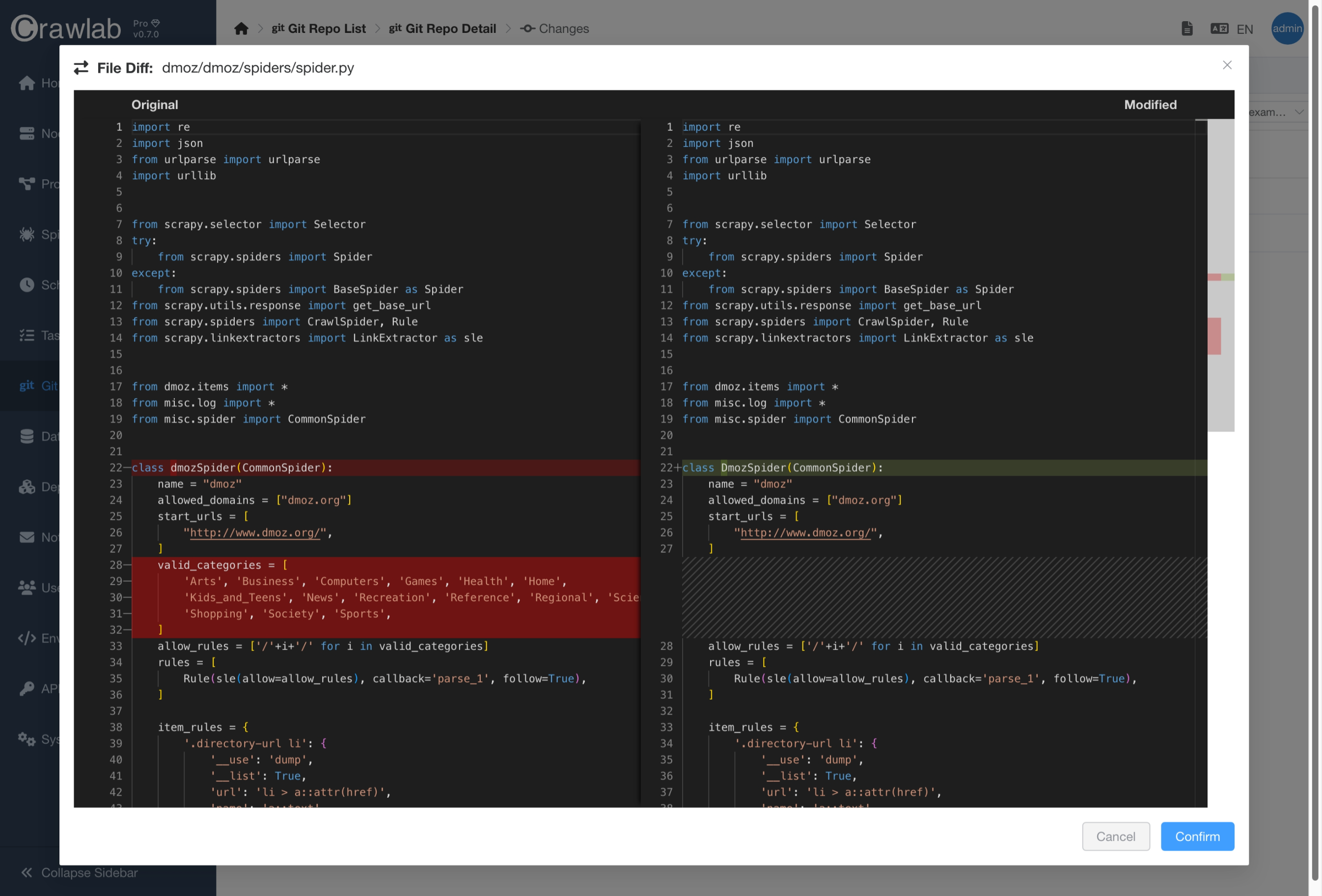
Push Code
You can push the changes to the remote repository by clicking the Push button in the branch selection dropdown or in
the Changes tab.
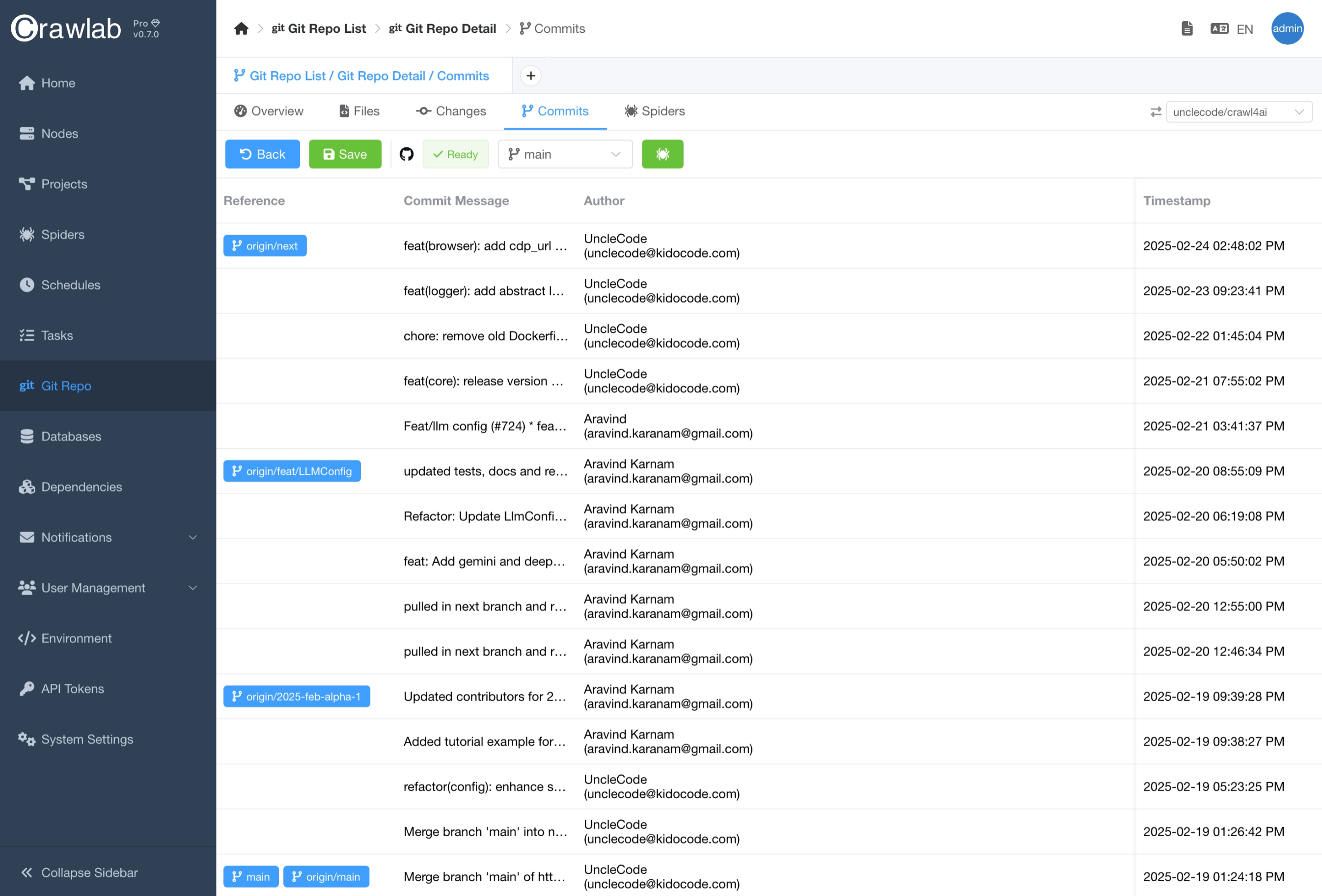
View Git Commits
You can view the git commits (logs) by clicking the Commits tab.
Git Integration
Crawlab Git integration allows you to create and manage spiders from Git repositories, which enables version control and team collaboration on multi-spider projects.
Create Spider
You can create a spider linked to a Git repository.
- Navigate to the
Git Repodetail page. - Click the
Create Spiderbutton. - Enter necessary information for the spider.
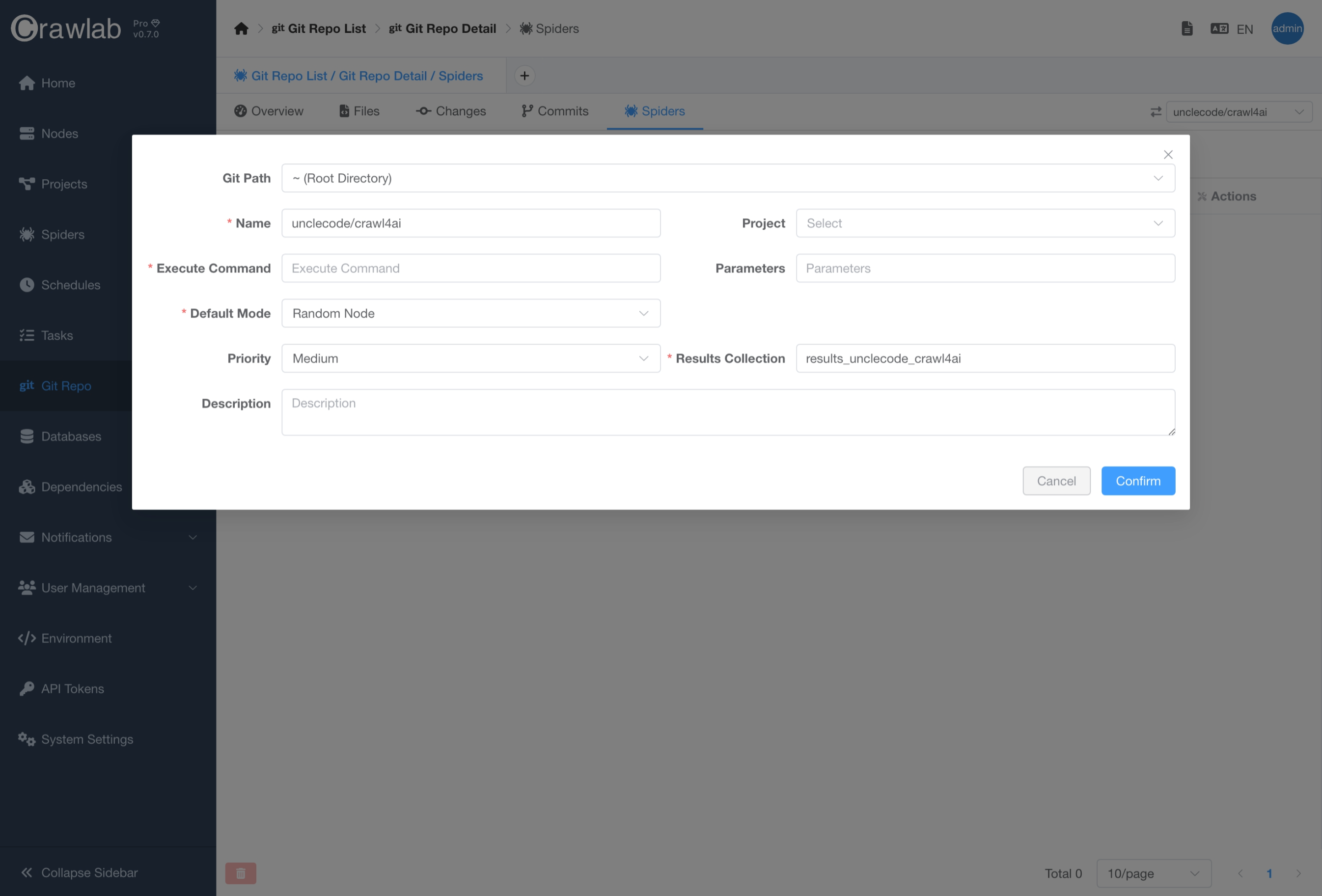
- Click the
Confirmbutton. - The created spider can be viewed in the
Spiderstab.
Alternatively, you can create a spider from the Files tab.
- Navigate to the
Git Repodetail page. - Navigate to the
Filestab. - Right-click the directory you want to create a spider from and select
Create Spider.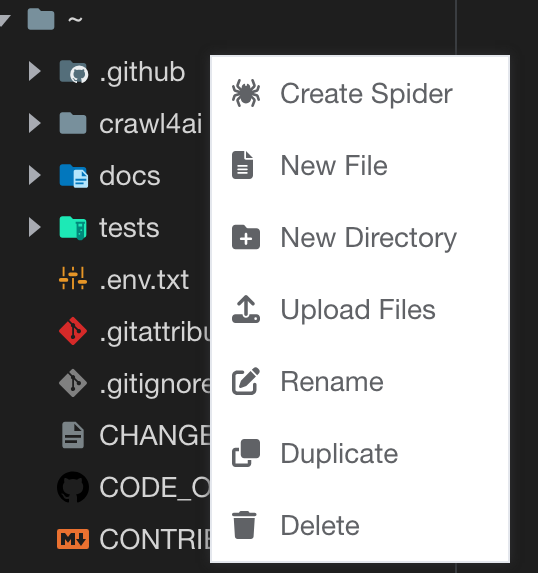
- Enter necessary information for the spider.
Spider Sync
You don't have to manually update spiders when you make changes to the code in the Git repository. Crawlab will automatically sync the spiders with the latest code in the Git repository.
Typical Workflow
The typical git integration workflow with in Crawlab is as following diagram.
As you can see, the workflow is quite simple. You can create/update spiders from the local Git repository, and the spiders will be crawled by the Crawlab server. You can also pull the latest code from the remote Git repository to the local Git repository and push your changes to the remote Git repository from Crawlab if you have edited the code in Crawlab.